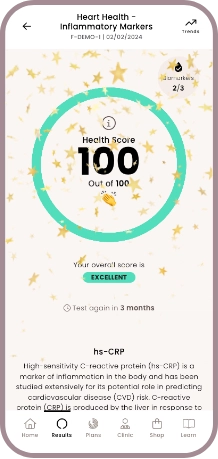
- Health scores calculated
Close
About flexible subscriptions
How does a subscription work?
When you purchase this test subscription plan, we will automatically send you another test kit in a few months. Don't worry - you have full control over when this will be, and you can change/cancel it anytime.
When you first purchase this test, you can choose your subscription options in the checkout. We do this, because we recommend taking multiple tests over time to track how your biomarkers change. You'll be charged per test kit (rather than monthly, for example).
Why subscribe to multiple tests?
One test will show you what areas you need to focus on, continued testing will help you learn how your training, diet and lifestyle is impacting your health.
How often should I test?
We recommend a follow up test 3 months after your first test, followed by a test every 6 months depending on your results, but its up to you!
Can I change what's tested in future tests?
Yes, you can tailor/customise subsequent tests (via your app) to focus on just the areas that need improving.
Ultimate Health Check
Our Ultimate health check is an at-home blood test that gives you a full health assessment by checking 47 health markers covering heart health, liver & kidney function, thyroid function, muscle function, nutrition, immune health, hormones and more.
Validated & analysed by NHS Lab
Phlebotomy kit (venous sample)
Doctor reviewed
Results in 15 working days
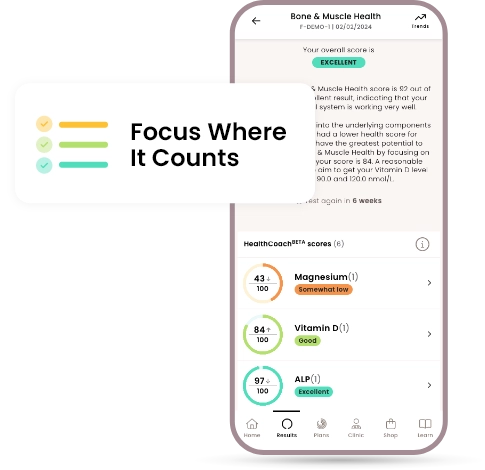
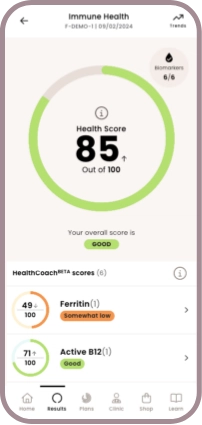
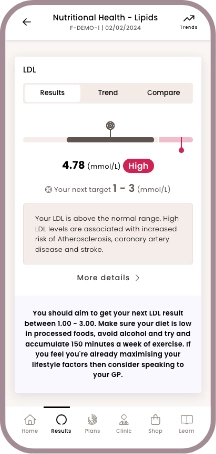
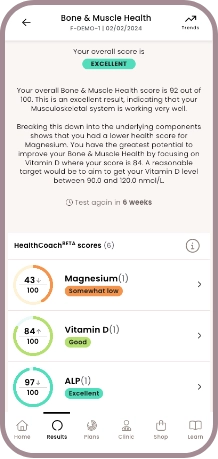
Health scores
£399
3 Interest-free payments
Learn more
Shop now. Pay over time with Klarna
Klarna available at checkout.
Klarna's Pay in 3 / Pay in 30 days are unregulated credit agreements. Borrowing more than you can afford or paying late may negatively impact your financial status and ability to obtain credit. 18+, UK residents only. Subject to status. Ts&Cs and late fees apply.
What gets tested?
47 Biomarkers
Blood sample collection options
How does it work?
When do I take the test?
Ideally, collect your blood sample within 3 hours of waking and before food. Due to the amount of blood required for analysis, the sample needs to be taken from your vein by a healthcare professional. This can be done in your own home or by visiting our partner clinic. You can choose the best option for you during checkout.
Certified for quality & security
Blood sample collection options
You can choose your preferred collection method when you checkout
Home nurse appointment (+£60)
We'll arrange for a medical professional to visit your home and collect your sample. This is great if you're unsure on how it all works or have trouble collecting a sample. No need to book a doctor's appointment or visit a clinic, we'll send you everything you need to collect a sample and post it back to our labs.
Visit a partner clinic (+£45)
Once you've ordered your test, look out for an email from our phlebotomy partners containing information and a link to book your appointment. We'll send you everything the clinic will need to complete the sample and post it back to our labs.
Organise a nurse myself (FREE)
If none of the above options work for you, you can arrange your own medical professional to collect your sample. There is no additional charge for this. Once you've ordered your test, we'll send you everything you and your chosen medical professional will need to collect a sample and post it back to our labs.
Still unsure how it works? You can find more information on collection methods and the service we provide in our 'How it Works' section.
How does it work?

1. Choose your blood test
No need to wait for a GP appointment, choose from our wide range of tests which come with everything you need to take your sample and return to our lab.

2. Collect your sample
Take your finger prick blood sample at home, or choose to have your blood taken at a Superdrug health clinic or a nurse at home. Return to our NHS lab using our prepaid envelope.
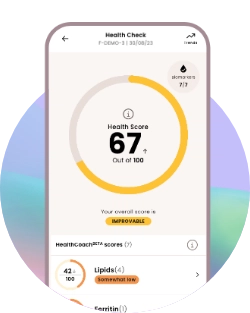
3. View your results
View your results on your secure health dashboard within 2 working days of our lab receiving your sample. Read personalised comments from our GPs.
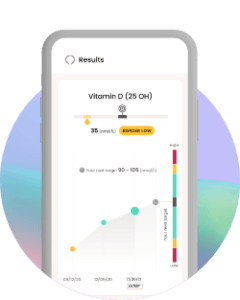
4. Make improvements
With more in-depth results, you will be able to identify areas that need improving. Make the changes and track your progress.
What gets tested?
47 Biomarkers Included
- Active B12
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
- Albumin
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
- Corrected Calcium
- Chloride
- Cortisol (9am)
- Creatine Kinase
- Creatinine
- eGFR
- Ferritin
- Folate (serum)
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Free Androgen Index
- Free Testosterone
- Testosterone (Total)
- Gamma GT
- Globulin
- Haemoglobin
- HbA1c
- HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
- HDL Ratio
- hs-CRP
- LDL
- Luteinising Hormone (LH)
- Magnesium (serum)
- Oestradiol (Oestrogen)
- Omega 6: Omega 3 Ratio
- Progesterone
- Prolactin
- Red Blood Cell (RBC)
- Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin
- Sodium
- Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TG)
- Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPO)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Thyroxine (T4 free direct)
- Total Cholesterol
- Total Protein
- Triglycerides
- Triiodothyronine (T3 free)
- Urea
- Uric Acid
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D (25 OH)
- Vitamin E
- White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
Additional biomarkers can be added by personalising this test.
What are biomarkers?
Biomarkers are specific compounds we can detect in your blood sample that reflect different things about your health. Your test will tell you your levels for each of the above biomarkers, and whether they are in a normal range.
Unlock your health scores with HealthCoach™
Powered by cutting-edge technology, Forth’s industry leading app goes beyond reporting basic biomarker results and one-size-fits-all health advice to deliver a comprehensive roadmap to better health.
Your Ultimate Health Check will give you the following Health Scores
Nutritional health
Immune health
Liver health
Heart health
Bone & muscle
Hormone health
Mental health
Metabolic health
Kidney health
Thyroid health
Why do the Ultimate test?
Our Ultimate blood test can help you assess all key areas of your health. It’s the perfect way to focus on areas that need improvement or give you peace of mind that your lifestyle is supporting your overall health and wellbeing. This test has a 15-day turnaround time from lab to results due to some markers needing analysis at a specialist lab.
What does the Ultimate Health Check test?
The ultimate health check is our most comprehensive blood test, checking 47 biomarkers across 7 health areas – heart health, nutrition, mental health, liver and kidney health, muscle & bone and hormone health. You’ll get the best understanding of your health and what might be causing you to feel tired, or constantly poorly.
Frequently asked questions
This is what our customers ask us most about this test. For more information, try our help centre.
When will I get my results?
We aim to deliver your results within 15 working days of your blood sample arriving at our lab. The reason it takes this amount of time is due to some of the health markers requiring analysis at a specialised lab.
How do I view my results?
When you buy your test, we will ask you to create an account with us during checkout. This will give you access to your own, secure health dashboard where you can view your results.
How secure is my data?
We have strict processes in place to ensure the protection of your data. Following GDPR the company also operates under tight legal rules about the sharing of data which ensures that data is only shared if it is crucial to the delivery of our service. For example, our doctors see customer results at the time of review, however, after review, access to results is withdrawn.
Can I do a finger prick blood sample?
Due to the amount of blood needed to analyse all the health markers in this test, we cannot offer it as a finger prick blood test.
How do I find out my results are ready?
We keep you updated throughout the process by email and text message.
We will let you know when your blood sample has arrived at our lab. Once the blood sample has been analysed one of our doctors will review your results.
Once your results are ready, we will email you and send you a text message to let you know your results are ready for you to view in your health dashboard.
Important information regarding corrected calcium
Our labs have conducted stability validation on all the markers offered by Forth. Corrected Calcium has a shorter stability time than the majority of markers of around 2 – 3 days. Forth provides a Tracked 24 return envelope in all kits to return samples to the lab within 24 hours. In the majority of cases, samples are returned within the stability time. If a sample arrives outside this time, this result will not be provided to you.
How is my blood sample taken?
Due to the amount of blood needed to analyse all the health markers in this test, we need a blood sample taken from your vein, known as a phlebotomy blood sample.
We offer 3 options for taking your blood sample from your vein:
- You can arrange to have your blood sample taken by a nurse in your own home. We will provide you with the details to book a home appointment once you’ve ordered your test.
- The second option is to visit your nearest Phlebotomy clinic to have your blood taken by a nurse. You can find your nearest clinic during checkout.
- The final option is to arrange the blood draw yourself either at your local doctor’s surgery or hospital if they provide that service.
The sample kit we send you will contain everything you need to have your blood sample taken.
How soon will the test arrive?
If you order your test before midday on a Monday to Friday then your kit will be dispatched
the same day.
All our kits are sent out via Royal Mail first class post, so it should be with you within 1-2
working days.
How secure is my data?
We have strict processes in place to ensure the protection of your data. Following GDPR the company also operates under tight legal rules about the sharing of data which ensures that data is only shared if it is crucial to the delivery of our service. For example, our doctors see customer results at the time of review, however, after review, access to results is withdrawn.
Learn more about your data security.
Can I have someone take my blood for me?
Yes. We offer two options if you do not want to do our finger prick test. The first is a home appointment where a nurse comes to your home to take a blood sample. The second is to visit a Phlebotomy clinic near you that offers a blood sample service.
A blood sample will be taken from your vein and we will provide you with everything you need to give to the nurse to allow them to take the sample.
The nurse will give you the blood sample to return to us using the pre-paid envelope provided.
Does a doctor review my results?
We have a team of doctors and nurses who look at all results and will comment on any results that are outside of the normal range for your age.
Can I download the results to share with my GP?
Yes, you can download your results from your health dashboard as a PDF to share with your GP.
Learn how to export your results.
We are dedicated to supporting you on improving your health
Go to help center
Ultimate Health Check, recommended by our doctors
"The Ultimate Health Check is our most complete test, looking extensively into your health and wellbeing markers. It is an exhaustive combination of biomarkers that give our clinicians incredible insight into your current and future health. Not only identifying current nutritional deficiencies but establishing your long term risk factors for serious medical conditions including atherosclerosis, heart disease, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia and metabolic dysfunction."
Dr Thom Phillips
Similar tests
We're changing people's lives
How our Ultimate Health Check works
Getting the insights you need to improve your health has never been easier.

1. Order your blood test
Order your home blood test and we'll deliver it straight to your letterbox.

2. Make an appointment
Choose whether to have a nurse come to your home to take your blood sample, or visit one of our partner clinics.

3. Post sample
As soon as your blood is drawn, pop your sample in the post to us using the Tracked-24 envelope supplied.

4. View your results
With more in-depth results, you will be able to identify areas that need improving. Make the changes and track your progress.
What's included in this test?

Blood sample kit
Results within 15 working days
Tracked 24 delivery & return
Secure health dashboard
Accredited lab analysis
Doctor reviewed results
Our impact in numbers...
70+
From hormones to nutrients, we offer 70+ different tests
60,000+
We've helped over 60,000 people improve their health
800,000+
We've delivered over 800,000 test results
Related articles
Like this article? Here are some more based on similar topics.
Ultimate Health Check