12 mins read
How To Improve Home Blood Test Results
- Blood Test Results Explained
- Why Track Health Biomarkers?
- Vitamin D
- Folate
- Ferritin
- Cholesterol
- Triglycerides
- Low Vitamin B12 Levels
- Low Vitamin D Levels
- Low Folate (B9) Levels
- Low Ferritin Levels
- Low Levels Of Cholesterol
- Low Levels Of Triglycerides
Blood Test Results Explained
Whether your results are within the normal range or outside, it can be hard to know what to do with the insight you’ve gained.
We take a look at some of the key biomarkers in our tests and provide tips on how to improve results that are outside the normal ranges. As well as advice on why you should keep tracking even if your results are normal.
Why Track Health Biomarkers?
Tracking biomarkers can help you identify areas of your health that need improvement. For example, you can check biomarkers key to energy, mood, immune health and general wellbeing. You can find out more on the benefits of tracking biomarkers in our blog on health optimisation.
The biomarkers key to overall wellbeing include vitamin B12, vitamin D, folate, ferritin, cholesterol and triglycerides. These all contribute to our energy levels, mood and improve our immune and heart health. Let’s take a look at each in a bit more detail:
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is known as an essential nutrient which means the body is unable to produce it, so we must get it through our diet. It is key to the normal function of the brain and nervous system as well as the formation of red blood cells and helps to create DNA. Vitamin B12 enables the release of energy by aiding the body in the absorption of folic acid (folate/B9).
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is needed for the absorption of calcium in the gut and helps to maintain optimal calcium and phosphate levels within the body to enable normal bone mineralisation to prevent involuntary muscle contraction known as hypocalcaemia tetany. It also plays a role in reducing inflammation within the body, supporting cell growth, neuromuscular and immune function as well as the metabolism of glucose.
Folate
Folate, or vitamin B9 is another essential nutrient we can only get through our diet. It works with B12 to produce healthy red blood cells, the formation of DNA and to enable nerves to function effectively.
Ferritin
Ferritin is a blood protein that contains iron and is a good indicator for the amount of iron the body stores. It makes iron available for cellular processes in the body and protects lipids, DNA and proteins from the potentially toxic effects of iron1.
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is essential to helping produce cell membranes in all tissues and organs within the body, so it pretty crucial! It is also key to the production of hormones. Cholesterol is produced by the liver and we also get cholesterol from our diet. There are two types of cholesterol, LDL which is the bad kind and HDL which is the good kind. High levels of LDL are a risk factor for heart disease.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood and is the body’s main storage of fat which it uses for energy. Like cholesterol, it is made by the liver and we can also get it through diet. High levels of triglycerides increase the risk of developing heart disease.
How To Improve Low Blood Test Results
The blood test results range from low to high and are based on an average, so regular testing will help identify what is normal for you and your body.
Blood test results that come back below the normal range expected for your age and gender can be worrying. However, any results outside of the normal range will be reviewed by one of our healthcare professionals and advice will be offered. But let’s take a closer look at what you can do to improve low levels of vitamins B12, D, folate and ferritin.
Low Vitamin B12 Levels
The average level of vitamin B12 in women is 114 pmol/L and 111 pmol/L for men, with the normal range being anything between 37.5 pmol/L and 188 pmol/L.
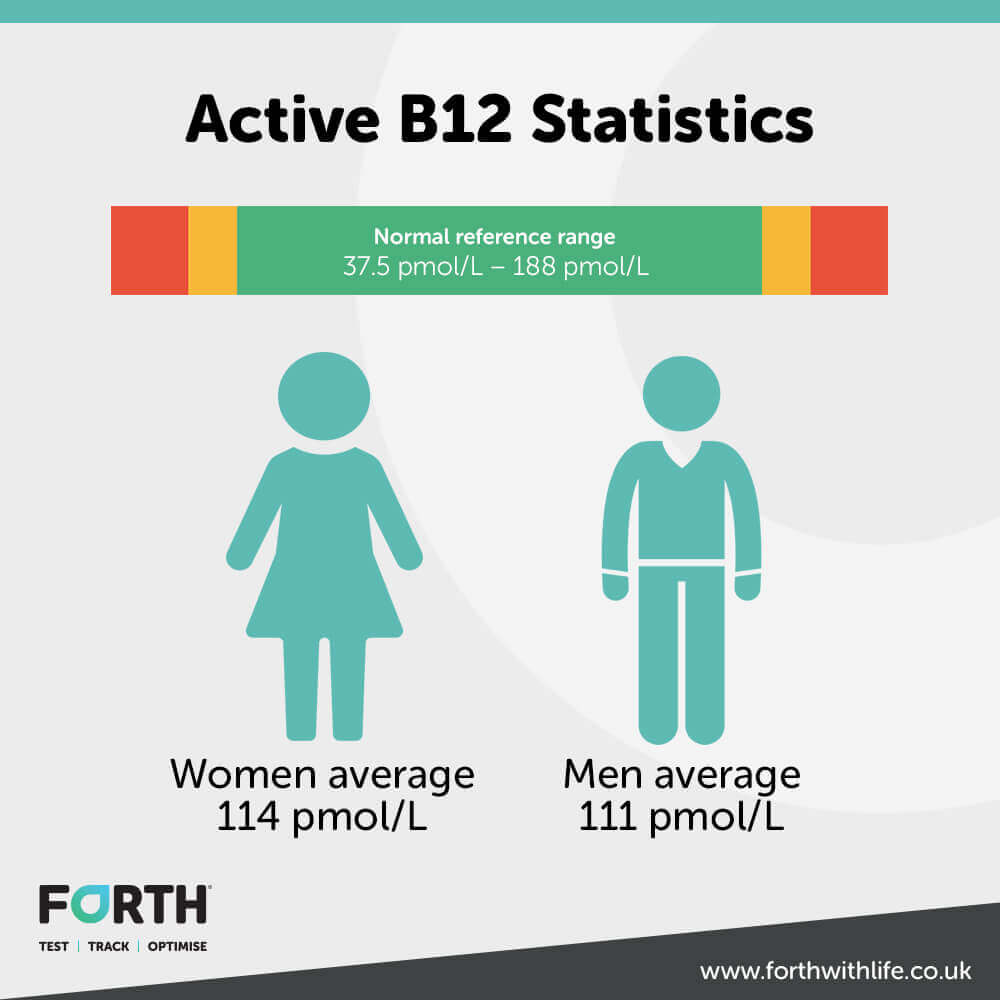
Any result lower than 37.5 pmol/L is considered in the lower range of normal and needs addressing.
Symptoms of Low Vitamin B12
Having low vitamin B12 levels can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency, the symptoms of which include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Constipation
- Confusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is often caused by malabsorption of food, anaemia, or a diet deficient in good sources of B12.
How To Increase Vitamin B12 Levels
The best way to increase your vitamin B12 levels is through diet. Although depending on your results you may be advised to take a supplement. Good sources of B12 include beef, chicken, trout, salmon, cheese, milk, yogurt and eggs. Try to avoid taking too much vitamin C as this can limit the absorption of B12. According to NHS guidelines adults (those over 18 years of age), need 1.5 micrograms of B12 a day.
Read more about foods that are rich in vitamin B12.
Low Vitamin D Levels
In one of our studies into vitamin D deficiency we found that 74% of people have vitamin D levels below the optimum level for good health. The optimum level of vitamin D is between 75 nmol/L and 175 nmol/L. Anything below 50 nmol/L is considered insufficient and levels <25 nmol/L is considered deficient.
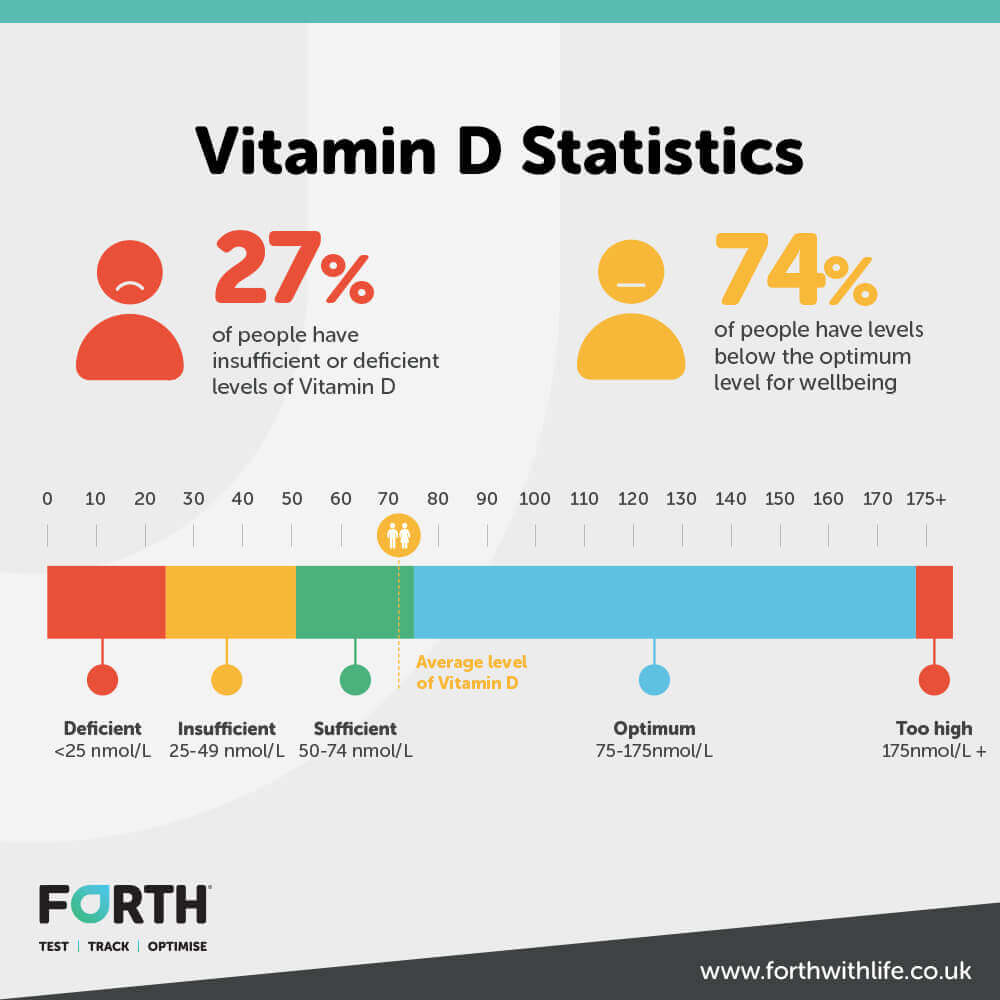
Most adults in the UK are deficient in vitamin D, particularly during the winter months when more time is spent in doors and the sun we do get is weaker.
Symptoms of Low Vitamin D
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include:
- Depression
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- Muscle pain
- Recurrent infections
- Bone pain
How To Increase Vitamin D Levels
There are two ways to increase your vitamin D levels, one is through the absorption of sunlight through the skin and the other is through diet.
During winter months the NHS advises that all adults should take 10 micrograms (400ui) of vitamin D a day between October and March to prevent vitamin D deficiency. If you are deficient then taking 1000ui a day of vitamin D3 between tests should bring your levels back up. However, do seek medical advice on how much you need to take based on your results – our doctor should provide you with this information as part of their comments on your results.
Read more about vitamin D deficiency.
Low Folate (B9) Levels
The average level of folate is between 8.83 nmol/L and 60.8 nmol/L with the average result being 21.9 nmol/L. Results below the average level is considered low.
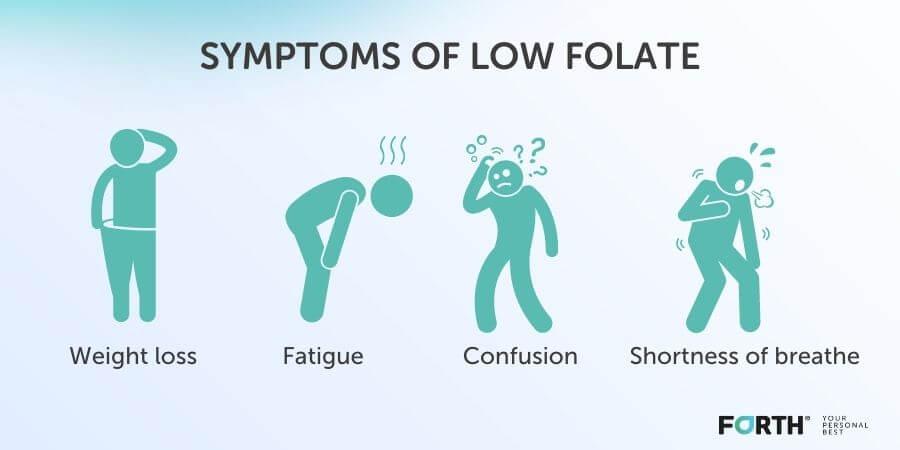
Symptoms of Low Folate
Folate levels are analysed alongside vitamin B12 as both biomarkers can indicate macrocytic anaemia. This is where red blood cells are unable to carry oxygen as efficiently and can result in large red blood cells. Symptoms of macrocytic anaemia are:
- Loss of appetite or weight
- Brittle nails
- Fast heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Diarrhoea
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Poor concentration or confusion
How To Increase Folate Levels
Folate can only be obtained through food, although in some cases a supplement may be recommended (generally in pregnant women). Good sources of folate include green, leafy vegetables such as kale, cabbage and spinach, wholegrain foods, chickpeas and kidney beans and liver.
Low Ferritin Levels
The normal range of ferritin within the body is between 13µg/L and 150µg/L. Borderline low levels are between 12-13µg/L, anything below 12µg/L is considered low. Low ferritin levels can be an indicator for iron deficiency anaemia.
Symptoms Of Low Ferritin Levels
The main symptoms of low ferritin levels include:
- Pale skin
- Fatigue
- Very low energy levels
- Headaches
- Difficulty breathing
- Dry skin and hair
- Restless leg syndrome
- Increased heartbeat
How To Increase Ferritin Levels
The best way to increase iron levels is through diet, although you may be advised by a doctor to take a supplement depending on your results. The best sources of iron are liver, red meat, beans (kidney beans, chickpeas, butter beans etc), lentils, nuts, seeds, dried fruit, spinach, kale and swiss chard (dark green leafy veg). According to NHS guidelines, adult women should consume 14.8mg of iron a day (but only 8.7mg a day over the age of 50), and men over the age of 18 should consume 8.7mg per day.
Low Levels Of Cholesterol
Total cholesterol levels in healthy adults should be 5 mmol/L or less. LDL levels should be 3 mmol/L and HDL levels should be above 1 mmol/L. Total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels should be low, but low HDL levels can increase the risk of heart disease as it plays a role in ridding the body of LDL cholesterol (the bad kind).
Symptoms of Low Cholesterol
Cholesterol levels should be low, but very low cholesterol levels that aren’t low due to medication should be investigated. Although more research needs to be carried out there is evidence that very low cholesterol levels can have a negative impact on mental health2. A study found that young women with low cholesterol were more likely to suffer from anxiety and depression. It is thought that this could be due to cholesterol’s role in producing hormones and low levels may affect brain function. However, low levels are not common, the biggest issue in the Western world is high cholesterol levels.
How To Increase HDL Levels
Eating food high in fibre, fatty fish such as salmon, olive oil, whole grains, beans and nuts will all help to increase your levels of HDL. Physical exercise will also help raise your HDL levels.
Low Levels Of Triglycerides
The normal level of triglycerides in the body are less than 1.7 mmol/L. Like cholesterol, it’s good to have low levels of triglycerides in the body to reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Symptoms Of Low Triglyceride Levels
There isn’t a range for low triglycerides, however, a very low result may need further investigation as it could indicate an underlying health condition.
Recipes To Increase Biomarker Levels
Below are a selection of recipes to help increase, or maintain, your levels of B12, folate and iron.
- Boiled Eggs & Asparagus Soldiers (Jamie Oliver)
- Silky Masala Eggs (Jamie Oliver)
- Greek Yogurt Breakfast Bowls (Modern Honey)
- Pan Fried Trout with Bacon, Almonds and Beetroot (BBC Good Food)
- Teriyaki Salmon With Sesame Pak Choi (BBC Good Food)
- Herb Omelette With Fried Potatoes (BBC Good Food)
- Mediterranean Chicken Traybake (Olive Magazine)
- 15-Minute Go-To Healthy Beef and Broccoli (A Sweet Pea Chef)
- Sweet Potato Hash With Feta And Eggs (The Gluten Free Blogger)
- Chilli Con Carne (BBC Good Food)
- Sausage, Roasted Veg & Puy Lentils One-Pot (BBC Good Food)
- Jerk Chicken And Mango Bowl (BBC Good Food)
- Lentil Bolognese (I Heart Eating)
- Spinach And Ricotta Cannelloni (Jamie Oliver)
- Herby Chickpea Balls With Tomato Sauce (BBC Good Food)
- Easy Three Bean Chilli (The Simple Veganista)
How To Improve High Blood Test Results
High Levels Of Vitamin B12
It is not common to have naturally high vitamin B12 levels, however, high B12 levels without supplementation could be indicative of an underlying health condition such as liver or kidney problems or diabetes, so should be investigated further.
High Levels Of Vitamin D
Again, unless over supplementing, vitamin D levels are not naturally high. You can suffer from vitamin D toxicity if you take too much vitamin D supplement, signs of vitamin D toxicity include:
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Headaches
- High blood pressure
- Kidney stones
- Calcium toxicity
High Levels Of Folate
Having high folate levels does not generally cause the body any problems, however, it can indicate vitamin B12 deficiency.
High Total Cholesterol Levels
Mildly high cholesterol levels are between 5mmol/L and 6.4mmol/L, moderately high is between 6.5mmol/L and 7.8mmol/L and very high cholesterol is above 7.8mmol/L. You doctor will be able to advise you of the best course of action if your cholesterol levels are raised.
In some cases, changing your diet to one that is low in saturated fats, salt and sugar, and high in unsaturated fats, fibre, whole grains and pulses will be enough to bring your cholesterol down. If not, your doctor may prescribe medication.
High Triglyceride Levels
Borderline high levels of triglycerides are between 1.8 to 2.2 mmol/L, high is between 2.3 to 5.6 mmol/L and very high is anything above 5.7 mmol/L. If you have high triglycerides it increases your risk of heart disease, especially if LDL cholesterol levels are high as well.
The most common cause of high triglycerides are obesity and poorly controlled diabetes. Losing weight and improving your diet will help improve levels if you are overweight and better management of diabetes will also help lower levels. If your levels are high you should seek advise from your GP.
High Levels Of Ferritin
High ferritin levels could be a sign of iron overload which may be due to an inherited condition called haemochromatosis which can cause:
- Fatigue or feeling tired all the time
- Feeling weak
- Joint pain
- Weight loss
- Women may have irregular periods
- Men may find it difficult to get or keep an erection
Other causes of high ferritin levels include obesity, kidney failure, inflammation, liver problems and rheumatoid arthritis.
High levels should be investigated further by seeing your GP.
Your Levels Are Within The Normal Range
If your levels are all within the normal range than you can be pretty pleased that you are in good shape. However, if you took the test to investigate reasons for particular symptoms then you should visit your GP to investigate further.
Otherwise, it’s important to continue to track your levels. Why? Because we are all unique individuals, so although there are recommended ranges for the levels of our body’s biomarkers there can be a lot of variation between individuals. That’s why it’s important to establish your own, personal biomarker profile so you know what’s normal for you.
Taking more than one test will:
- Allow you to develop a clear picture of your own unique biological profile and determine what ‘normal’ is for you.
- Allow you to accurately measure what lifestyle changes have the greatest impact on your health, and target those specifically.
- Identify any changes early on.
The more data points you have, the better our experts can identify the Critical Difference Threshold for you, and therefore decide whether a significant physiological change has happened.
The more regularly you test, the clearer the picture of your performance and health, and the more accurately we can help you identify issues before they become problems.
Conclusion
Tracking biomarkers key to health will help you identify whether your lifestyle and diet are providing you with everything you need to be at your best. It will enable you to make improvements if your results are low or high based on your age and gender, as well as enabling you to build up your own personal biomarker profile. This will help you identify any changes over time, so if your results come back normal today, retesting will help identify any changes early so you can make the right adjustments to your diet and lifestyle.
By understanding your levels of biomarkers key to overall wellbeing will help you proactively manage your health, improving your energy, heart health, bone health, immune system, mood and much more.
- Health scores calculated
Close
This information has been medically reviewed by Dr Thom Phillips
Thom works in NHS general practice and has a decade of experience working in both male and female elite sport. He has a background in exercise physiology and has published research into fatigue biomarkers.

Dr Thom Phillips
Head of Clinical Services
Related articles
Like this article? Here are some more based on similar topics.





